Theory: Methodological Skills
| Site: | DIGITOUR Training Platform |
| Course: | Building Digitalisation Readiness in the Tourism SME Sector - ENGLISH |
| Book: | Theory: Methodological Skills |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 9 February 2026, 2:09 AM |
1. Introduction
Methodological skills are essential in any field, from business and science to daily life. As a matter of fact, they are much needed in the tourism sector, where additionally to the factors that are valid for any sector, there are specificities, like the close relation with people, the dependence of the sector on factors like the weather climate conditions, the geopolitical tensions etc., the provision of supplementary services to state just a few of them.
The methodological skills enable individuals to make concrete decisions, manage risks, and think critically in the face of complex problems. They are especially important in today's rapidly changing world, where new challenges arise constantly yet require quick and effective responses. Below are some of the most typical methodological skills.

In the following we are giving the definitions and main characteristics of the above methodological skills.
Decision making is a key component of methodological skills. It involves analysing information, evaluating options, and selecting the best course of action based on the available data. Effective decision making is a crucial skill that is essential for success in both personal and professional settings. It involves several processes, such as identifying the problem, gathering information, evaluating options, and selecting the best course of action based on the available data.
In addition to decision making, risk management is another critical skill that is vital in many fields. This skill involves assessing potential risks, implementing strategies to minimize those risks, and monitoring the effectiveness of those strategies over time.
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks in order to minimize their impact on an organization or individual. It is an essential skill that should apply to any complex or uncertain environment. Effective risk management involves understanding the nature and severity of potential risks, developing strategies to minimize or avoid those risks, and implementing those strategies in a systematic and proactive manner. In this bitesize, we will explore the key concepts and principles of risk management, including risk assessment, risk mitigation, and risk monitoring.
Critical thinking is another important aspect of methodological skills. It involves analysing information from multiple sources, evaluating arguments and evidence, and forming well-reasoned judgments. Critical thinking is crucial for making informed decisions and solving complex problems, as well as for identifying and dealing with biases and assumptions.
Communication is a fundamental skill that is essential for success in both personal and professional contexts. Communication skills involve the ability to convey information, thoughts, and ideas clearly and effectively, while also being able to listen actively and respond appropriately. Strong communication skills can help individuals build strong relationships, resolve conflicts, and collaborate effectively with others. Effective communication skills can also help individuals advance in their careers, as they are essential for successful teamwork, leadership, and public speaking. Moreover, good communication skills can contribute to personal growth and development by improving self-expression, self-awareness, and empathy. In today's digital age, communication skills have become even more crucial as individuals must navigate various forms of technology and social media platforms to interact with others. Overall, strong communication skills are a valuable asset in both personal and professional settings and are essential for success in today's world.
Collaboration is a vital skill that is essential for success in both personal and professional settings. Collaboration skills involve the ability to work effectively with others towards a common goal, sharing ideas, resources, and expertise. Strong collaboration skills are essential in today's globalized and interconnected world, where teams are often composed of individuals from diverse backgrounds and cultures. Effective collaboration skills involve active listening, open-mindedness, and the ability to communicate ideas and feedback in a constructive and respectful manner. Strong collaboration skills can lead to enhanced creativity, problem-solving, and innovation, as individuals can draw on the strengths and perspectives of others. In the workplace, strong collaboration skills are essential for effective teamwork and leadership, as well as for building strong relationships with colleagues and clients. In personal contexts, collaboration skills can facilitate the development of strong friendships, partnerships, and networks. Overall, collaboration skills are an important asset that can help individuals navigate complex challenges and achieve success in both personal and professional contexts.
To sum it up, in this bitesize we will examine how methodological skills can be developed and applied in various contexts, and we will provide practical tips and strategies for enhancing these skills. By the end of this bitesize, you will have a deeper understanding on how to use methodological skills to make better decisions, manage risks more effectively, approach problems with a more critical and analytical mindset and communicate and collaborate in a more efficient way.
2. Decision making
Introduction
To build or not a beach bar opens also to externa customers in our hotel? To offer or not light lunch in the pool bar or just refreshments and drinks? What to do to resolve the problem of cleaning the pool from leaves of the nearby plane tree? These are just three indicative situations that require to make a decision. In business, decision-making is a crucial part of any operation. Depending on the level at which the decision is made, there are three primary types of decisions: strategic, tactical, and operational. Each of these decisions differs in terms of their scope, time horizon, and impact on the organization.
Strategic decisions are high-level decisions that are made by top-level executives. These decisions are focused on the long-term goals and direction of the organization, e.g. to establish a new airline connection abroad, to introduce a new guided tour, to build a new aisle in the hotel with suites and an individual pool for each suite. Strategic decisions are typically made infrequently and have a significant impact on the organization. Examples of strategic decisions include mergers and acquisitions, diversification of products or services, and market entry or exit decisions.
Tactical decisions are made by middle managers and are focused on implementing the strategies set by top-level executives. Tactical decisions are made more frequently than strategic decisions and are generally focused on achieving short to medium-term goals. Examples of tactical decisions include hiring decisions, marketing campaigns, and product development decisions. In the tourism sector examples are hiring a new Japanese chef, following the strategic decision to find a sushi restaurant, to launch a social media campaign following the decision to offer a new guided tour, etc.
Operational decisions are made by front-line employees and are focused on day-to-day activities. These decisions are made more frequently than strategic and tactical decisions and are focused on achieving immediate goals. Examples of operational decisions include scheduling employees, ordering inventory, and resolving customer complaints. Examples of tactical decisions in the tourism sector are the contents of the tiny basket in toilets of a hotel, uniforms of staff in a restaurant, frequency of change of the menu etc.
In summary, strategic, tactical, and operational decisions are essential to the success of any organization. Each decision is made at a different level of the organization and has a different time horizon, scope, and impact on the organization. Understanding these different types of decisions is critical for effective decision-making and ultimately, organizational success.
Principles of Decision Making
To make a good decision, it is important to have clear and well-defined goals that align with your values and priorities. It is essential to consider all possible options or courses of action and weigh their pros and cons. Gathering relevant and accurate information and analysing it objectively are critical steps in making an informed decision. Every decision involves trade-offs and opportunity costs, and it is important to consider these factors in the decision-making process. Every decision involves some degree of risk and uncertainty, and it is important to assess and manage these factors appropriately.
Decision Making Techniques
There are several techniques that can be used to make effective decisions. Rational decision making involves identifying the problem, collecting relevant information, generating alternatives, evaluating each alternative based on a set of criteria, and selecting the best one.
Some types of Decision-making are:
● Intuitive decision making involves relying on your instinct or gut feeling to make a decision, based on your past experiences and expertise. This type of decision relies upon the experience and talent of a specific person, more frequently of the manager, but have to take some time to be made, because even if the brilliant idea has come in a flash, it requires time to examine all parameters to make the decision work.
● Rational decision making is the opposite of intuitive decision making. It is a strict procedure utilising objective knowledge and logic. It involves identifying the problem to solve, gathering facts, identifying options and outcomes, analysing them, considering all the relationships and selecting the optimal decision. Even in this case, some phases of this procedure, as for example the identification of options, which is a creative activity and the ways to transmit enthusiasm to persons involved to make the decision a success, are not purely rational procedures.
● Heuristics are mental shortcuts that can help simplify complex decision-making tasks, but they can also lead to biases and errors if not used appropriately. The main problem of heuristics, which are based on how one acted in analogous cases in the past (e.g. difficult customers), is that it does not give the time or effort to conceive an entirely new and more creative solution, which could prove to be much more beneficial.
● Individual decision making is commonly accepted as an effective way of making up your mind on something, since you are focused and able to make prompt decisions. In a hotel the decisionmaker may be the manager. As the hotel manager is in many cases the owner and in others the person responsible in front of the owners, he/she often tends to make decisions by him/herself. It is however a problem when the manager demands that he/she has to be asked even for the slightest decisions e.g. if windows have to be opened, the music to be more aloud or not etc.
● Group decision making is about involving multiple stakeholders in the decision-making process, which can provide diverse perspectives and improve the quality of the decision. In many cases managers miss a lot of information that other members of staff in direct contact with customers may have.
Challenges of Decision Making
There are several challenges and pitfalls that can hinder effective decision making. People tend to be overconfident in their ability to make accurate predictions or judgments, which can actually lead to poor decisions.
- Confirmation bias is a tendency to seek out information that confirms existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them, which can lead to narrow-minded decisions.
- Escalation of commitment is a tendency to become more committed to a decision once time, money, or effort has been invested, which can lead to stubbornness and reluctance to change course.
- Group decision making can be affected by group thinking, which is a tendency to conform to the group's consensus and ignore dissenting opinions.
Decision making in tourism
Tourism is a delicate set of product, susceptible to a variety of factors including the decisions of powerful international tourism agencies that channel a great portion of tourism flows. Decision-making in tourism involves navigating through uncertain environments, considering stakeholder interests, and balancing short-term goals with long-term sustainability. Analytical thinking and problem-solving skills are necessary for identifying and defining problems, gathering relevant information, and generating solutions. Data-driven decision-making utilizes market trends and customer preferences to make evidence-based choices. Nowadays, many touristic companies including airlines, airports, car rentals, hotels etc., use quality management systems like ISO 9001 and collect, process analyze the opinions and remarks of customers as a standard procedure to gain insight of the quality of their services.
Risk assessment tools, such as SWOT analysis and scenario planning, help manage potential risks. Stakeholder engagement ensures diverse perspectives are considered for inclusive and sustainable outcomes. Ethical and sustainable decision-making prioritizes social, environmental, and cultural impacts. Adaptability and flexibility are essential for adjusting strategies in response to evolving trends and challenges.
Conclusion
Effective decision making is a complex and critical skill that can be developed and improved with practice and reflection. By applying the principles and techniques discussed in this chapter and being aware of the challenges and pitfalls, you can make informed and ethical decisions that align with your goals and values.
3. Risk management
Introduction
The occurrence of the covid 19 epidemy in 2019-2020 and the imposed personal isolation produced a shock for the tourism industry, which had disastrous effects for the whole sector and persons employed in it internationally. This fact has put a pressure to companies to think about measures to ensure the business continuity.
Of course risk was not a
new-born concept. Risk is an inevitable part of both personal and
business life and inherent factor in all entrepreneurship. To
avoid adverse consequences and attain favourable results, it is
crucial to handle risks efficiently. Risk management is a
systematic approach that involves identifying, evaluating, and
mitigating potential risks that can impact individuals or
organizations. This process entails assessing the likelihood and
potential consequences of risks and devising measures to minimize
their probability or impact. For example, the likelihood of
occurrence of a problem if you use the remnants of a dinner
buffet to include them in next morning’s breakfast may be low, if
the food is kept following the correct rules. The severity of
consequences though may be very high if a customer gets food
poisoning. In this chapter, we will delve into the fundamental
principles, methods, and difficulties of risk
management.
Principles of Risk Management:
The first step in risk management is to identify and define the risks that could impact an organization or individual. Risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk and prioritizing them based on their severity. Risk mitigation involves developing and implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate the likelihood or impact of risks. Risk monitoring and review involve regularly assessing and updating the risk management plan to ensure its effectiveness and relevance.
Risk Management Techniques
There are several techniques that can be used to manage risks effectively. Risk management involves avoiding activities or situations that could lead to potential perils. An example may be offering discount prices for booking some months in advance and applying severe refund rules to mitigate the risk of a non-previewed even occurring to affect tourism (e.g. a terrorist attack in that city) or having an individual power generator to face potential blackouts during summer. Risk reduction involves implementing measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of risks, such as applying safety procedures or redundancies. Risk management also involves transferring the risk to another party, such as through insurance or contracts. Risk management additionally involves accepting the risk and developing contingency plans to mitigate its impact if it occurs.
Risk Management Process Description
The project risk management process defines the activities to identify, assess, prioritise, manage and control risks that may affect the execution of the project and the achievement of its objectives. This process is divided into four steps:
Step 1: Risk Identification
The purpose of this step is to facilitate the identification and documentation of risks that can impact the project objectives e.g. the risk not to find trained staff for the summer period, the risk the chef of the cuisine leaves you at the middle of the touristic period etc.
Various techniques will be used for risk identification which typically focus on past trends or future exposure, on a bottom-up or a top-down analysis.
Some organisations have a Risk Typology that groups various types of risks into categories and it will be used as reference, e.g. risks related to force majeure (for example due to bad weather, geopolitical tensions etc.), due to the lack (or quitting) of the adequate personnel, to an event that impacts badly the reputation of the location as tourist destination, to bad competition, to infrastructure problems etc.
Risks are continuously identified throughout the project lifecycle; however, very early during the Initiating phase, an initial risk list will be created which is thereafter frequently updated.
Step 2: Risk Assessment
The purpose of this step is to assess the likelihood and impact of the identified risks in terms of their influence on the project objectives. This assessment is necessary before any risk response planning can be done.
Risks are assessed based on their likelihood of occurrence and the impact on project objectives. The product of their likelihood and impact defines the Risk Level, which is then used as a reference for their prioritisation and risk response development.
Depending on the stakeholders' risk appetite, evaluation scales and tolerances will be defined based on which the most appropriate risk response strategies are chosen.
Step 3: Risk Response Development
The purpose of this step is to select the best risk response strategy and identify and plan the actions to control the risks.
The selection of the risk response strategy will be based on the results of the risk assessment (risk level), the type of risk, on the effects on the overall project objectives (e.g. schedule and costs), as well as on the cost of the strategy and its benefits (cost/benefit analysis). The strategy (or strategies) selected for each risk are documented in the Risk Log.
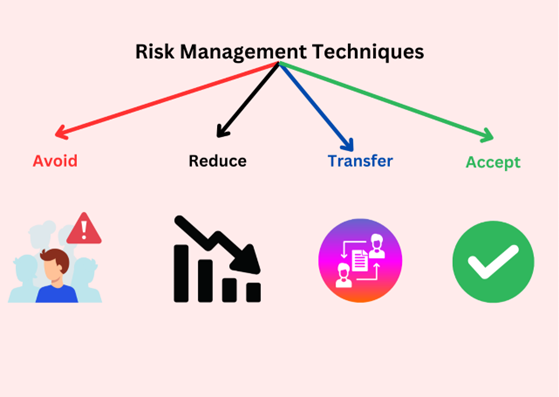
There are four strategies to be considered as risk responses: Reduce, Avoid, Transfer, or Accept a risk. For the risks that have been accepted, contingency plans may be applied to help control their impact in case they occur.
After the strategy for each risk has been selected, specific actions to implement the strategy will be defined, described, scheduled and assigned (e.g., self-owned generator for blackouts, private fresh water tank for water shortages, lifeguard shifts for swimming safely, training to newly appointed staff etc.), while a Risk Owner assumes the responsibility for its implementation.
Actions will detail concrete activities, milestones and deliverables and will be documented in the Risk Log. Moreover, they will clearly identify the target resolution date, as well as the estimation of resources involved and dependencies. These actions (at least the most effort/cost consuming ones) will be incorporated into the Project Work Plan, to have a consolidated view of all project related activities.
Step 4: Risk Control
The purpose of this step is to monitor and control the implementation of the risk response activities while continuously monitoring the project environment for new risks or changes (e.g. probability and/or impact) in the risks already identified.
The Project Follow-up Meetings are used to revise the status of risks and related actions, and to identify new risks that may have a negative impact on project milestones, deliverables or objectives.
Challenges of Risk Management
There are several challenges and obstacles that can hinder effective risk management. One of the main challenges is uncertainty, as risks are inherently unpredictable and can have unforeseen consequences. Limited resources and competing priorities can also make it difficult to allocate sufficient resources to risk management activities. Resistance to change and complacency can lead to a lack of urgency or commitment to risk management. In addition, the complexity of modern organizations and systems can make it difficult to identify and evaluate all potential risks.
Case study
A case study about risk management from a resort in Malaysia:
Conclusion
Effective risk management is essential for achieving desired outcomes and avoiding negative consequences. By applying the principles and techniques discussed in this chapter and being aware of the challenges and obstacles, individuals and organizations can develop a proactive and comprehensive approach to risk management. By continuously monitoring and reviewing the risk management plan, and adapting it as necessary, individuals and organizations can minimize the likelihood and impact of risks and achieve their goals.
4. Critical thinking
Introduction
Critical thinking is an essential skill that enables individuals to analyse information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions. It involves a systematic and objective approach to reasoning that considers multiple perspectives, evaluates evidence and assumptions, and identifies underlying assumptions and biases. In this chapter, we will discuss the principles, techniques, and challenges of critical thinking.
Principles of Critical Thinking
The first principle of critical thinking is to approach information and arguments objectively, without preconceived biases or assumptions. It is essential to identify and evaluate the credibility and reliability of sources of information and to recognize the limitations of one's own knowledge and expertise. Critical thinking also involves analysing and evaluating arguments, considering the underlying assumptions, evaluating the evidence presented, and identifying logical fallacies or weaknesses in reasoning.
Techniques for Critical Thinking
There are several techniques that can be used to develop critical thinking skills. Analysing and evaluating arguments involves identifying the premises, the conclusions, and the reasoning connecting them. It is essential to identify the evidence supporting the premises and the logical structure of the argument. It is also important to evaluate the strength of the evidence and identify any biases or assumptions that may undermine the argument. Distinguishing between correlation and causation involves recognizing the difference between events that occur together and events that are causally related. It is essential to consider alternative explanations and evaluate the plausibility and strength of each explanation.
Challenges of Critical Thinking
There are several challenges and obstacles that can hinder effective critical thinking. One of the main challenges is cognitive biases, which are unconscious mental shortcuts that can lead to errors in reasoning and decision making. In the tourism sector, where one often deals with foreign people, this in many cases involves stereotypes about ethnicities or external appearance to predict customer behaviour, which is obviously non rational and wrong. Confirmation bias is a tendency to seek out information that confirms existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them. Availability bias is a tendency to rely on information that is readily available or easily accessible, rather than seeking out all relevant information. Overconfidence bias is a tendency to be overly confident in one's own judgments and abilities.
Conclusion
Effective critical thinking is essential for making informed decisions and evaluating information and arguments objectively. By applying the principles and techniques discussed in this chapter and being aware of the challenges and obstacles, individuals can develop a systematic and objective approach to reasoning and decision making. By recognizing and minimizing cognitive biases, individuals can avoid errors in reasoning and make more accurate and informed decisions. Critical thinking is an ongoing process that requires continuous practice and reflection, and it is a skill that can be developed and improved over time.
5. Communication skills
Introduction
Communication skills have been identified as one of the crucial factors of modern businesses, and this has been confirmed by numerous studies conducted so far (Goby, Citation2007; Halfhill & Nielsen, Citation2007; Lim et al., Citation2016; Plant & Slippers, Citation2015; Robles, Citation2012; Shuayto, Citation2013; Wang et al., Citation2009; Zehrer & Mössenlechner, Citation2009).
Tourism is a sector that is based, apart from the weather conditions, the beautiful environment and the culture, on the close contact and growing or warm relations between people.
Although professional knowledge is essential for work efficiency, research shows that possessing only technical skills has become insufficient to meet the challenges of today's business environment (Robles, Citation2012).
Namely, employers are no longer interested in individuals who possess only specific technical skills but lack other significant skills, particularly soft skills (Binsaeed et al., Citation2016).
According to Andrews and Higson (Citation2008), soft skills refer to interpersonal skills, dealing with people and attitudes, which enhance business efficiency and interpersonal relations.
Effective communication is crucial for the success of any business, particularly in the service industry where it is essential. Communication is even more important in the tourism and hospitality industry where it goes beyond just conveying information and plays a deeper role in interactions between employees and tourists. Research suggests that communication is the most important soft skill in tourism and hospitality, with hospitality managers spending up to 80% of their day communicating with others. The quality of their communication has a significant impact on employee job satisfaction. The employees who directly interact with guests are considered the most important, and a reversed pyramid organizational structure has been proposed to reflect this. To maintain a positive business environment, all tourism employees must be capable of communicating effectively with guests, colleagues, and stakeholders at all levels.
Written and oral communication skills
While research on the importance of communication skills is growing, studies examining the way messages are conveyed are relatively few. Most studies have focused on written and oral communication skills, which are essential for literacy and business communication. However, some studies suggest that young employees lack sufficient oral communication skills. While there are multiple scales for written and oral communication skills developed for various professions and stakeholders, they may not be enough to meet modern business needs. Therefore, there is a need to expand the communication skills set. In tourism oral communication is the most often form of communication, although there customers have to be also given some critical information in written e.g. safety instructions, services provided, menus with pricelists, rules of dressing, behaviour etc. Because in the tourism sector much communication may take place with foreigners it is needed that written instructions may also be available in one or more foreign languages and use signs and photos as much as possible. Persons mastering foreign languages are also a must in tourism companies.
Listening skills
Listening skills are crucial in interpersonal communication, and research shows that managers spend a significant portion of their workday listening. Listening involves receiving, interpreting, and responding to messages, and it is considered the most important and frequent communication activity in business. However, listening skills are often neglected as they are considered a natural process, unlike hearing which is purely physical. Listening efficiency is low, with only 25% to 50% of the spoken information being effectively processed. Brownell (1996) developed a framework for listening skills that includes six major components, which can be used as a tool for assessing listening skills.
Non-verbal communication skills
Effective communication involves multiple dimensions and attributes, including nonverbal elements that can enhance or alter the meaning of verbal messages. Although verbal communication skills receive the most attention from researchers, Drucker (1989, as cited in Ratcliffe, 2016) emphasizes the importance of paying attention to nonverbal cues, as they can convey significant information.
Nonverbal communication, which includes the communication environment, physical characteristics of the communicator, and body movements, is estimated to account for up to 70% of total communication (Barnum & Wolniansky, Citation1989, as cited in Sundaram & Webster, Citation2000).
This is particularly relevant in the service industry, where the physical appearance of personnel can influence customers' perception of their professionalism and trustworthiness (Sundaram & Webster, Citation2000). However, measuring nonverbal communication is challenging due to its complexity. Researchers have developed scales to measure nonverbal communication, but there is no consensus on how to operationalize these skills.
For example, Uzun (Citation2017) developed a comprehensive scale, while Leigh and Summers (Citation2002) and Limbu et al. (Citation2016) focused on nonverbal cues in sales contexts, and Lolli (Citation2013a) narrowed the scope to nonverbal skills relevant in the hospitality industry. Despite their importance, nonverbal communication skills remain understudied.
Another important factor in the tourism sector is that people coming from different parts of the world may use different body language codes to express the same thing, or worse, to use the same code to express different things. One has to be aware of this problem as this may cause misunderstandings and unnecessary problems.
Digital skills[1]
The modern business environment, digitalization, and social media growth point to the need for developing new communication skills that follow the technological changes of contemporary business but go beyond technical and computer skills (Van Laar et al., Citation2017).
In this digital world, writing is more important than ever because digital media require more written communication and employees' skills are always exposed to the public due to the influence of the Internet (Guffey & Loewy, Citation2016). Moore and Morton (Citation2017) stressed the inability to adapt the message to a particular situational context, where new employees lack adequate communication skills.
Digital literacy goes beyond the ability to use digital devices and software; it requires a range of cognitive, motor, social, and emotional skills to function effectively in a digital environment. The transparency of the internet makes communication skills even more important, as they are exposed to the public. Digital communication skills are now necessary in classical communication tools as well, as modern media allow for two-way communication at three levels. This area is expected to grow significantly in the future, requiring a higher level of competency and precise definition of the necessary skills.
Communication skills in tourism
Recruiting and continuously training employees in the tourism and hospitality industry is crucial due to the significant role communication skills play in generating positive interactions with customers (Cuic Tankovic, 2020). Communication is a vital aspect of daily operations in the tourism business, both externally with customers and internally among employees (Brownell, 2016; Lolli, 2013a).
Internal communication reinforces employee satisfaction, which ultimately impacts guest satisfaction (Ryan et al., 1996). It involves the exchange of ideas, information, instructions, and coordination of activities within the organization (Guffey & Loewy, 2010). Effective internal communication helps in developing products and services, as well as evaluating and rewarding employees.
Interpersonal communication in tourism is characterized by personal connectivity and takes into account the specific psychological characteristics of individuals (Burleson, 2010). It is a two-way communication process that often occurs through direct personal contact. Interpersonal communication is highly significant for all parties involved in the tourism process.
The importance of communication skills has been emphasized in various tourism studies, highlighting them as essential skills for future employees in the industry (Wang et al., 2009; Zehrer & Mössenlechner, 2009). However, some studies indicate that new tourism employees often lack sufficient communication skills (Lolli, 2013b; Stevens, 2005; Paranto & Kelkar, 2000), emphasizing the need for further research in this area to enhance understanding. Despite the significance of communication skills for successful encounters in tourism, several authors have identified significant deficiencies in the communication skills of tourism employees (Peterson, 1997; Bednar & Olney, 1987).
Conclusion [2]
In conclusion, effective communication skills are essential for success in modern businesses. While technical knowledge is necessary, possessing soft skills, particularly communication skills, is equally important. Communication skills include written and oral communication, listening skills, nonverbal communication, and digital skills, all of which play a crucial role in business communication. The tourism and hospitality industry is particularly dependent on communication skills due to its focus on interactions between employees and tourists. As businesses continue to evolve in the digital age, digital literacy and digital communication skills have become increasingly crucial. Developing and honing communication skills can enhance business efficiency, employee job satisfaction, and positive interactions with stakeholders.
[1] There is a specific bitesize in this eLearning Tool called “Digitalization & tourism” that explains Digital Skills in detail.
[2] If you wish to explore further the importance of Communication Skills, you may go to Module 3 “Digital Social Skills”
6. Collaborative skills
Introduction
Collaborative skills refer to the ability to work effectively with others towards a common goal. In today's dynamic and fast-paced business environment, the ability to collaborate is a crucial factor for success. The traditional concept of the individualistic approach to work has shifted, and companies now rely heavily on collaboration to achieve business objectives. The need for collaboration is particularly significant in service industries such as tourism and hospitality, where teamwork and customer service are essential for creating a positive customer experience. Collaboration is not limited to working within teams but extends to the collaboration between employees and customers, as they work together towards achieving a common goal. In this chapter, we will explore the importance of collaborative skills in the workplace, the benefits of effective collaboration, and the challenges that may arise during collaborative processes. We will also discuss the role of technology in enhancing collaboration and provide practical strategies for improving collaborative skills.
Importance of Collaborative Skills
Collaborative skills refer to the ability to work effectively with others, communicate clearly, and contribute to achieving common goals. In today's business environment, where organizations are increasingly complex and dynamic, collaboration has become a critical factor for success. Collaborative skills help organizations to work better, improve productivity, and increase innovation. By working together, employees can leverage their diverse skills, experiences, and perspectives to create new ideas and solutions. Collaborative skills also improve customer satisfaction by ensuring that all employees work together to meet customer needs.

Collaboration Between Employees
Collaboration between employees involves working together as a team to achieve common goals. It requires effective communication, trust, and mutual respect. Collaborative skills are necessary for effective teamwork, where each member brings their unique skills and experiences to contribute to the success of the team. Collaboration between employees can improve efficiency, productivity, and innovation. Collaborative skills are essential for employees in different departments, cross-functional teams, and remote teams. By collaborating effectively, employees can share knowledge and skills, overcome challenges, and create innovative solutions.
Conclusion
Collaborative skills are crucial for success in the modern business environment. They enable employees to work together effectively, improve productivity, and increase innovation. Collaboration between employees and customers is also essential for meeting customer needs and improving customer satisfaction. Developing collaborative skills requires a combination of training, practice, and feedback. By developing collaborative skills, organizations can create a collaborative culture that promotes teamwork, innovation, and customer satisfaction.