4. Critical thinking
Introduction
Critical thinking is an essential skill that enables individuals to analyse information, evaluate arguments, and make informed decisions. It involves a systematic and objective approach to reasoning that considers multiple perspectives, evaluates evidence and assumptions, and identifies underlying assumptions and biases. In this chapter, we will discuss the principles, techniques, and challenges of critical thinking.
Principles of Critical Thinking
The first principle of critical thinking is to approach information and arguments objectively, without preconceived biases or assumptions. It is essential to identify and evaluate the credibility and reliability of sources of information and to recognize the limitations of one's own knowledge and expertise. Critical thinking also involves analysing and evaluating arguments, considering the underlying assumptions, evaluating the evidence presented, and identifying logical fallacies or weaknesses in reasoning.
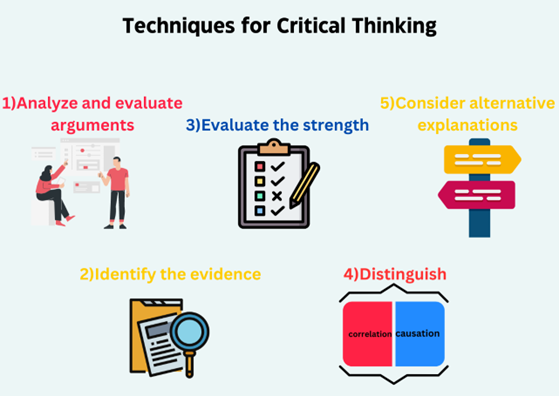
Techniques for Critical Thinking
There are several techniques that can be used to develop critical thinking skills. Analysing and evaluating arguments involves identifying the premises, the conclusions, and the reasoning connecting them. It is essential to identify the evidence supporting the premises and the logical structure of the argument. It is also important to evaluate the strength of the evidence and identify any biases or assumptions that may undermine the argument. Distinguishing between correlation and causation involves recognizing the difference between events that occur together and events that are causally related. It is essential to consider alternative explanations and evaluate the plausibility and strength of each explanation.
Challenges of Critical Thinking
There are several challenges and obstacles that can hinder effective critical thinking. One of the main challenges is cognitive biases, which are unconscious mental shortcuts that can lead to errors in reasoning and decision making. In the tourism sector, where one often deals with foreign people, this in many cases involves stereotypes about ethnicities or external appearance to predict customer behaviour, which is obviously non rational and wrong. Confirmation bias is a tendency to seek out information that confirms existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them. Availability bias is a tendency to rely on information that is readily available or easily accessible, rather than seeking out all relevant information. Overconfidence bias is a tendency to be overly confident in one's own judgments and abilities.
Conclusion
Effective critical thinking is essential for making informed decisions and evaluating information and arguments objectively. By applying the principles and techniques discussed in this chapter and being aware of the challenges and obstacles, individuals can develop a systematic and objective approach to reasoning and decision making. By recognizing and minimizing cognitive biases, individuals can avoid errors in reasoning and make more accurate and informed decisions. Critical thinking is an ongoing process that requires continuous practice and reflection, and it is a skill that can be developed and improved over time.