1. Introduction: Guiding Principles and Definitions
What is cyber security?
Definitions of cyber security vary, but in general, they all point to the security of cyberspace.
Cyber space is the dynamic and virtual space that connects different computer systems.
https://northafricapost.com/42416-morocco-is-not-a-cyber-jungle-defense-administration-tells-amnesty.html
Cyber security is made up of 2 key terms:
- Cyber relates to the technology which contains systems, network and/or data.
- Security relates to the protection which includes systems security, network security and application and information security.
The EU defines cyber security as “the activities necessary to protect network and information systems, the users of such systems, and other persons affected by cyber threats”.
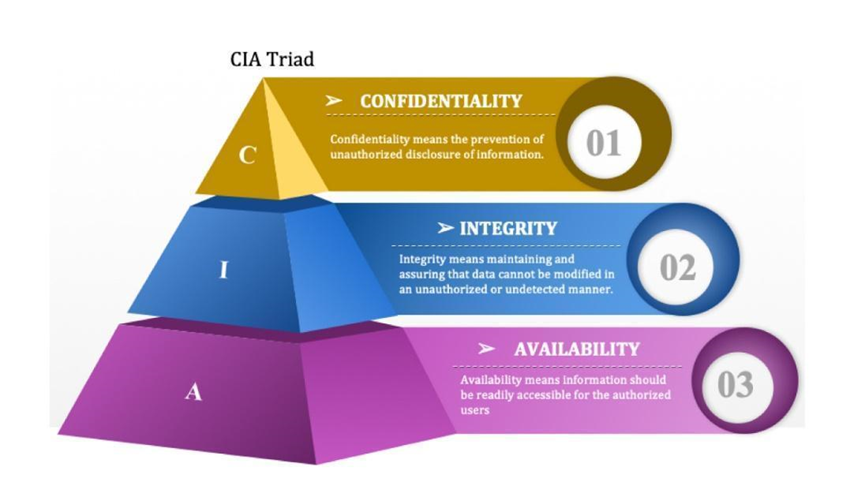
Confidentiality, integrity, and availability are known as the CIA triad, known as the 3 main principles of cyber security –
● Confidentiality: confidentiality measures prevent sensitive information from being disclosed to unauthorised access (e.g., data encryption, two-factor authentication).
● Integrity: integrity measures maintain the consistency, accuracy, and trustworthiness of data over the entire lifecycle by preventing data from being modified by unauthorised parties (e.g. data backups, using file permissions).
● Availability: availability measures ensure that information is consistently and readily accessible for the authorised parties in question and maintain the hardware and software systems that hold and display that information.
Overall, cyber security refers to every aspect of protecting an organisation and its employees and its assets against cyber threats or attacks.
https://thingscouplesdo.com/what-is-cia-triad-and-how-does-it-work/
What is cyber resilience?
In the business world, cyber resilience offers a more holistic way for digital business continuity. It is a new concept, referred to as digital fitness.
The EU defines cyber resilience as “the ability to protect electronic data and systems from cyberattacks, as well as to resume business operations quickly in case of a successful attack”.
In the sophisticated threat environment, traditional security tactics focused on cyber security are failing. No organisation can simultaneously sift through alters, track vulnerabilities, apply security policies across various systems.
To manage these competing challenges, organisations must change their security posture from a defensive stance focused on malware to a more realist and resilient approach – a cyber resilience approach (Symantec, 2014).
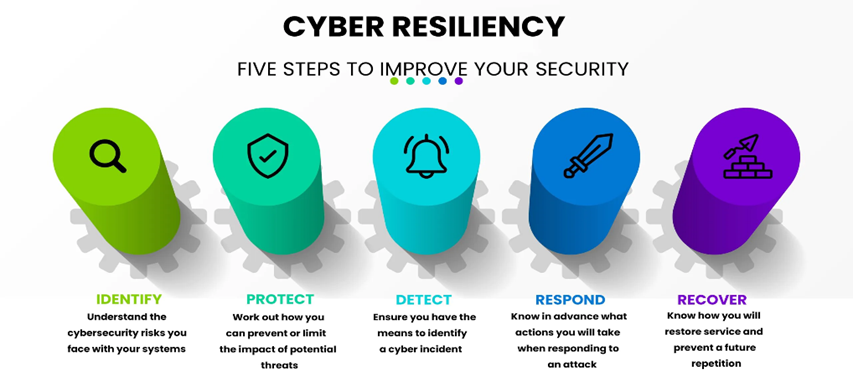
The concept of cyber resilience can be thought as of framework with 5 main pillars –
- Prepare/Identify: understanding the company’s security and identifying potential risk postures to address security vulnerabilities;
- Protect: understanding the company’s threat landscape (e.g. its level of vulnerability and risk tolerance) ensures protective infrastructure;
- Detect: once protective measures are in place, appropriate activities can be established to rapidly detect an attack, assess affected systems, and ensure a timely response;
- Respond: this phase is crucial to provide guidance on which activities can help accelerate the time to respond and contain the impact of an attack once it is detected;
https://www.amdhservicesltd.com/how-to-build-a-cyber-resilient-infrastructure
How are cyber security and cyber resilience linked?
Cyber security and cyber resilience may often appear interchangeable as they both relate to cyber safety, however, they are not the same thing:
⮚ Whilst cyber security refers to an organisation limiting its threats by focusing on proactive dispositions against the growing proliferation of cyberattacks;
⮚ Cyber resilience on the other hand refers to an organisation limiting as much as possible the potential damage and associated losses once an attack has already taken place while resuming business as usual.